Upper Control Limit Formula Standard Deviation
Confidence interval for Effect Size. If the trial is repeated 6 times and the chances of success for.
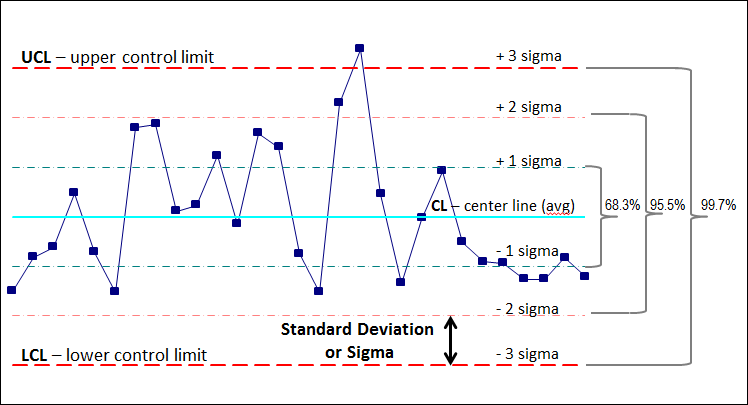
Control Chart Limits Ucl Lcl How To Calculate Control Limits
Use the standard control limit formula and the control chart table to calculate the control limits.
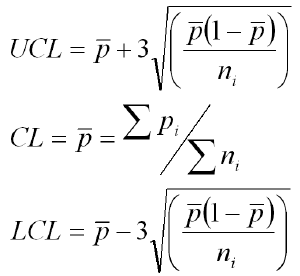
Upper control limit formula standard deviation. Additionally statisticians also refer to the empirical rule as the three-sigma rule because nearly all observations occur within three standard deviations. If your data follow a normal distribution you can easily determine where most of the values fall. The target SDI is 00 which indicates there is not any difference between the laboratory mean and the consensus.
By the way this may then beg the question - what is d2. Type UCL in cell D1 to specify the Upper Control Limit. Uncorrected sample standard deviation.
If a plotted point goes beyond the upper or lower control limit it can be. Enter the upper specification limit lower specification limit LSL process standard deviation and process mean in the process capability ratio calculator know the result. We subtract the AVERAGE CASES measure with the STDDEV.
Given here is the free online process capability index calculator to do a Cp and Cpk calculation for the given data. The formula for the population standard deviation of. The standard deviation is meaningful because its in the units of the variable and represents the standard difference between the observed values and the mean.
Lower limit on d. An upper bound on the standard deviation s is given by s 06R. So the Glass g statistic measures the difference in means in units of the control sample standard deviation.
It is driven by following formula. LCL is Lower control limit. The UCL is calculated by adding the average to 3 times the standard deviation.
Balphabeta Beta function. The formula for the pooled standard deviation is. The formula for standard deviation is v u u u t PN i1 x i 2 N 1 4 where x i is the measured value and x is the mean value and N is the number of observations in the sample.
The class of variable which can accept any value within the upper and lower limit is classified as. This rule sets a statistical control charts upper and lower limits at - three standard deviations. An estimate of the standard deviation for N 100 data taken to be approximately normal follows from the heuristic that 95 of the area under the normal curve lies roughly two standard deviations to either side of the.
Upper limit on d. Cohen recommended the following rule of thumb 02 small effect 05 medium effect 08 large effect However Cohen did. The upper control limit formula will vary depending on the statistic average range proportion count that is being plotted.
Ensure you are using the ri ght formula. Interpret X bar and S chart. In case of having upper and lower bounds as 1 and 0 beta distribution is called the standard beta distribution.
Upper and lower confidence limits are also shown in the Graph. In binomial distribution the formula of calculating standard deviation is. After selecting the Line GraphChart The X-Bar.
The formula for standard. UCL is Upper control limit. Refer common factors for various control charts.
Control limit formula will vary depending on the statistic average range proportion count being plotted. Enter the control mean standard deviation and the limits in the control limit calculator. Hedges g Cohens d and Glasss g are interpreted in the same way.
If a plotted point goes beyond the upper control limit it can be. The Bio-Rad Unity Interlaboratory Program uses the consensus group value as the target value. The average is easy to calculate and understand it is just the average of all the results.
One of the purposes of control charts is to estimate the average and standard deviation of a process. That would seem to make it a relatively intuitive measure by itself. But then consider the Empirical Rule.
To compute the upper control limit for the Range chart simply add the subgroup range values then divide by the number of subgroups to compute the average Range Rbar. The D4 constant contains an estimate of the standard deviation s multiplied by 3. Standard Deviation and Weighted Standard Deviation.
For LCL we do the opposite of UCL. Then multiply Rbar by D4 to compute the upper control limit. Type the following formula into this cell replacing B15 and B16 with cells containing your average and your standard deviation.
Traditionally after the discussion of the mean standard deviation degrees of freedom and variance the next step was to describe the normal distribution a frequency polygon in terms of the standard deviation gates The figure here is a representation of the frequency distribution of a large set of laboratory values obtained by measuring a single control material. In SlNo1 Select X-Bar X-Double Bar UCL LCL and then select Insert Option and next to Line Chart. 311 Plot X-Bar Chart.
Use the following formula to calculate the SDI. This is the last Step to plot the X-Bar Chart by using Line Graph in Excel follow the below steps as. Now that we have the standard deviation we can input this piece inside the UCL and LCL syntax.
Use the UCL to assess if there is a special cause on the high side. Sample 1 Sample 2. The standard deviation index is a measurement of bias how close your value is to the target value.
Find if the element is outside control limit using the ucl calculator. Best Regards Andrew Milivojevich. Use the control limits to assess if there is a special cause.
D2 is a correction factor with the ASSUMPTION of a normal distribution. Results CI using noncentral t distribution Hedges g Unbiased. For UCL we add the AVERAGE CASES measure with the STDDEV measure then multiply by 3 Hence 3 sigmas.
S bar is the average of all the standard deviation. In some cases it may not be appropriate to use a pooled estimate of standard deviation so the control group SD is used. We estimate a value for the standard deviation of the individuals by dividing the average range value by d2.
Example of Standard Deviation I Here if we calculate the standard deviation of your marks then x i is the individuals marks and x is the mean of class marks and N is the number of students. 2 square root of pq. Ensure you are using the right formula.
Effect Size based on control group SD. Use above Formula in excels. The statistical process control has the highest level of quality for a product in the ucl lcl calculator.
The below control chart constants are approximate values to measure the control limits for X bar S chart and other control charts based on subgroup size. The lower control limit lcl calculator finds the lower and upper limits of. Upper Control Limit UCL AVERAGE CASES STDEV3.
The standard deviation is a little more difficult to understand and to complicate things there are multiple ways that it can be determined each giving a different answer. 1 square root of p. In general this limit serves as a valuable way to identify outliers because 997 of all values should fall within it.
A b upper and lower bounds. The standard deviation gives an idea of how close the entire set of data is to the average value. A common source of confusion occurs when failing to distinguish clearly between the standard deviation of the population the standard deviation of the sample the standard deviation of the mean itself which is the standard error and the estimator of the standard deviation of the mean which is the most often calculated quantity and is also often colloquially called the.
Data sets with large standard deviations have data spread out over a wide range of values. The probability which explains x is equal to or less than particular value is classified as. LCL X Double Bar -3Standard Deviation.
In Statistical Process Control SPC we say that the processes are going normal if 9973 observations are scattered around the CentralControl Line within 3 standard deviations above and below the same thats why we calculate the upper limit as 3 standard deviation above from average which is a central line and lower limit as 3 standard deviations below of the average. In the above example n4. Data sets with a small standard deviation have tightly grouped precise data.
Conversion from g to r. Use the standard UCL formula and the control chart table to calculate the UCL. How to Calculate UCL Upper Control Limit LCL Lower Control Limit CL.
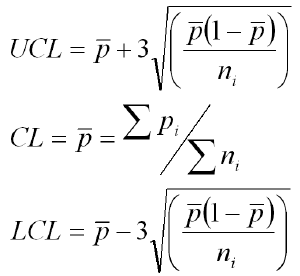
Control Chart Limits Ucl Lcl How To Calculate Control Limits
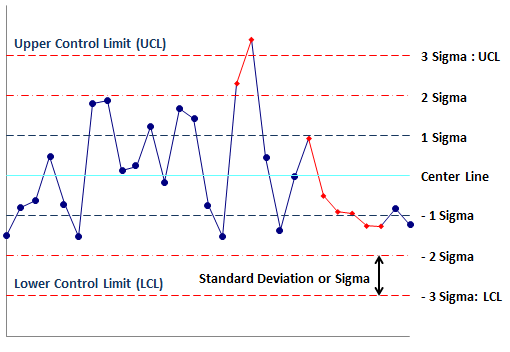
Control Chart Limits Ucl Lcl How To Calculate Control Limits

Calculating Control Limits For A C Chart By Hand Youtube
Posting Komentar untuk "Upper Control Limit Formula Standard Deviation"